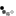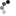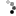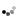Below are some of the key tyre patterns and an analysis of their strengths and weaknesses.
Rib shape: The main tread features are multiple circumferential grooves.
 |
- Advantages include lower rolling resistance plus good directional stability and steering control thanks to lateral resistance. Rib type patterns are suitable for sustained high speeds thanks to their low levels of heat generation.
- Key disadvantages are poor braking & acceleration grip on wet roads.
- Application: For paved road surfaces and truck or bus steer axles
|
Lug shape: Tread patterns with the groove arrangement perpendicular to the circumference of the tyre.
 |
- The main advantage of lug patterns is excellent braking power and traction.
- The biggest disadvantage is a tendency towards high noise when driven at high speed. Indeed, lug patterns are not suitable for high speed driving due to their high rolling resistance.
- Application: For dirt roads, rear wheels of buses, industrial vehicles and dump trucks.
|
Rib-Lug shape: A combination of Rib and Lug designs.
 |
- Key features are a rib in the centre providing directional control whilst a shoulder lug gives good braking & driving power.
- Application: Good for both paved and dirt roads. Usually used in both front & rear wheels of trucks and buses.
|
Block-shape: Patterns consisting of independent blocks divided by circumferential and lateral grooves.
 |
- Block patterns provide good steering control and stability on snow covered and wet roads as well as good water dispersal properties in the wet.
- However, because the tread blocks are smaller, tyre wear tends to be heavy.
- Application: Suitable for winter or all-season passenger car tyres as well as for the rear wheel use in ordinary applications.
|
Asymmetric pattern: Tread patterns which differ on either side of the tyre.
 |
- Asymmetric tyres have been designed to optimise the opposing requirements of dry grip and water dispersal. They are good for high speed cornering due to the greater contact area which helps reduce treadwear on outside of tyre.
- Asymmetric tyres must be positioned the right way around.
- Application: High performance and motorsport tyres.
|
Directional pattern: Tread patterns characterised by lateral grooves on both sides of the tyre which point in the same direction.
 |
- Advantages of directional tread patterns are good driving force and braking performance. In particular directional patterns provide good water dispersal meaning stability on wet roads.
- Directional tyres must be mounted in the direction of the tread pattern.
- Applications: Passenger car tyre for high speed use.
|
Tyre Information Disclaimer